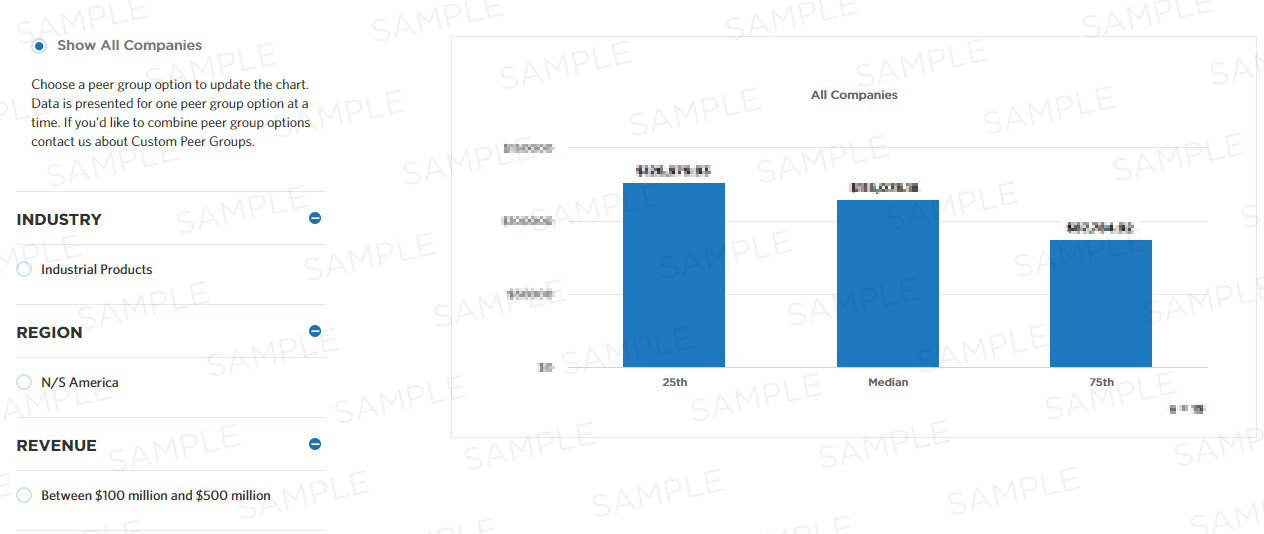
Total cost to perform the process group "generate and define new product/service ideas" per $1,000 revenue
This measure calculates total cost per $1,000 business entity revenue to perform the process group "generate and define new product/service ideas". Total cost is the sum of personnel (compensation/benefits), systems (direct and/or allocated), overhead (direct and/or allocated), other internal, and outsourced costs. The Process group "generate and define new product/service ideas" includes [Identifying and describing new product or service thoughts based on organizational objectives/targets.]. This Cost Effectiveness measure is intended to help companies understand this cost expenditure related to the process group "Generate and define new product/service ideas".
Benchmark Data
| 25th | Median | 75th |
|---|---|---|
| - | - | - |
Compute this Measure
Units for this measure are dollars.
(Total cost to perform the function "develop and manage products and services" * Percentage of total cost to perform the function "develop and manage products and services" allocated to the process group "generate and define new product/service ideas" * 0.01) / (Total business entity revenue * 0.0010)
Key Terms
Process Cost Components
Total cost for a process, process group, or function consists of the following five components.
Internal/In-house operating cost consists of the first four components (personnel, systems, overhead, and other).
Personnel Cost
Personnel cost is the cost associated with personnel compensation and fringe benefits of employees (i.e., those classified as FTEs which includes both full-time and salaried/hourly employees) contributing to each respective process. Personnel cost should include all of the following costs.
Employee Compensation: Includes salaries and wages, bonuses, overtime and benefits.
Fringe: Includes contributions made towards the employees' government retirement fund, workers compensation, insurance plans, savings plans, pension funds/retirement plans, and stock purchase plans. This should also include special allowances, such as relocation expenses and car allowances.
Systems Cost
Systems costs include all expenses, paid or incurred, in conjunction with:
Computer hardware or computer software acquired by the organization or provided to the organization through service contracts.
Any related costs to process, service and maintain computer hardware or computer software. The costs of providing and maintaining services for each applicable process (e.g., computer system(s) processing (CPU) time, network/system communication charges, maintenance costs for applications and data storage). This includes the costs related to LANs, WANs, etc. This does not include one-time costs for major new systems developments/replacements. Consultant fees should not be included in depreciation of new system implementations. Include only those costs that occur more than six (6) months after implementation, as normal system maintenance costs. Any systems cost (e.g., maintenance) which is outsourced to a third party supplier should be captured in the separate cost category labeled outsourced cost.
Systems cost should include all salaries, overtime, employee benefits, bonuses or fees paid to full-time, part-time or temporary employees or independent contractors who perform services relating to computer hardware, computer software, processing or systems support.
Overhead Costs
For the purpose of this study, provide the total actual overhead costs for the year related to the specified process. These are costs that cannot be identified as a direct cost of providing a product or a service. Include the primary allocated costs such as occupancy, facilities, utilities, maintenance costs, and other major costs allocated to the consuming departments. Exclude systems costs that are allocated, since these will be captured separately as systems cost.
Other Cost
Other costs are costs associated with the specified process, but not specifically covered in personnel cost, systems cost, overhead cost and outsourced cost in this questionnaire. These other costs include costs for supplies and office equipment, travel, training and seminars. Include the cost of telephones, except for that portion captured in systems cost.
External/Outsourced Cost
In determining outsourced cost, include the total cost of outsourcing all aspects of the specified process to a third-party supplier. Exclude one-time charges for any type of restructuring or reorganization. Outsourced costs should also include costs for intracompany outsourcing (i.e., reliance on a shared services center or other business entity).
Total Annual Revenue/Net Revenue
Total annual revenue is net proceeds generated from the sale of products or services. This should reflect the selling price less any allowances such as quantity, discounts, rebates and returns. If your business entity is a support unit and therefore does not directly generate revenue, then provide the revenue amount for the units you support. For government/non-profit organizations, please use your non-pass-through budget. For insurance companies the total annual revenue is the total amount of direct written premiums, excluding net investment income. Note: Business entity revenue needs to only include inter-company business segment revenue when the transactions between those business segments are intended to reflect an arm's length transfer price and would therefore meet the regulatory requirements for external revenue reporting.
Cost Effectiveness
Cost effectiveness measures are those in which two related variables, one of which is the cost and one of which is the related outcome related to the expenditure are used to determine a particular metric value.
Median
The metric value which represents the 50th percentile of a peer group. This could also be communicated as the metric value where half of the peer group sample shows lower performance than the expressed metric value or half of the peer group sample shows higher performance than the expressed metric value.