FTEs embedded in business groups or co-located with business end users as a percentage of KM FTEs
This measure calculates percentage of KM FTEs (Full Time Equivalents that directly support the knowledge management program, initiative, or service) that directly support your KM program, initiative, or service comes from embedded in business groups or co-located with business end users. This Supplemental Information measure is intended to help companies evaluate additional variables related to the process group "Develop enterprise-wide knowledge management (KM) capability".
Benchmark Data
Measure Category:
Supplemental Information
Measure ID:
108899
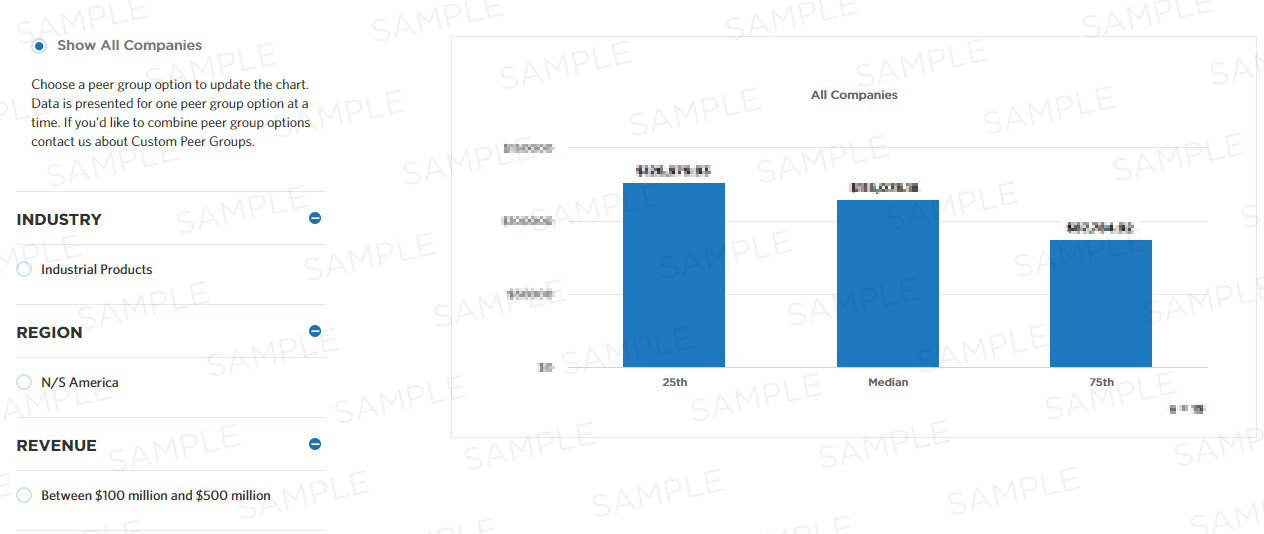
Total Sample Size:
284 All Companies
Performers:
| 25th | Median | 75th |
|---|---|---|
| - | - | - |
Key Performance Indicator:
Yes
Compute this Measure
Units for this measure are percent.
FTEs embedded in business groups or co-located with business end users
Key Terms
There are no key terms associated with this measure.