Why it is important to focus on change management in KM
Today we are watching our organizations deal with an overabundance of change. As Knowledge Management (KM) professionals, we strive to achieve a culture of knowledge sharing and collaboration through the implementation of KM strategies, approaches, processes and technologies. But we must stop and ask ourselves, are we adding to the change saturation and fatigue within our organizations? Or more positively, are we helping to alleviate employees feeling overwhelmed by incorporating good change management practices into our KM strategies and plans?
Change management can be described as the ability to proactively manage the “people side” of change and minimizing resistance through the use of standard processes and approaches to help transition employees, teams or an entire organization to a desired future state. At APQC, our 2023 KM priorities and predictions research ranked change management as the top skill for KM professionals to develop for the third year in a row. Click here if you would like to contribute to our 2024 priorities and predictions survey.
How to Effectively Manage Change
According to APQC’s research, six common practices in change management contribute to the success of any organizational change. And KM is no exception. Considering these approaches and ensuring change management is an ongoing part of your KM strategy will not only advance the maturity of your KM program but will ensure the desired behaviors are adopted and keeps employees engaged.
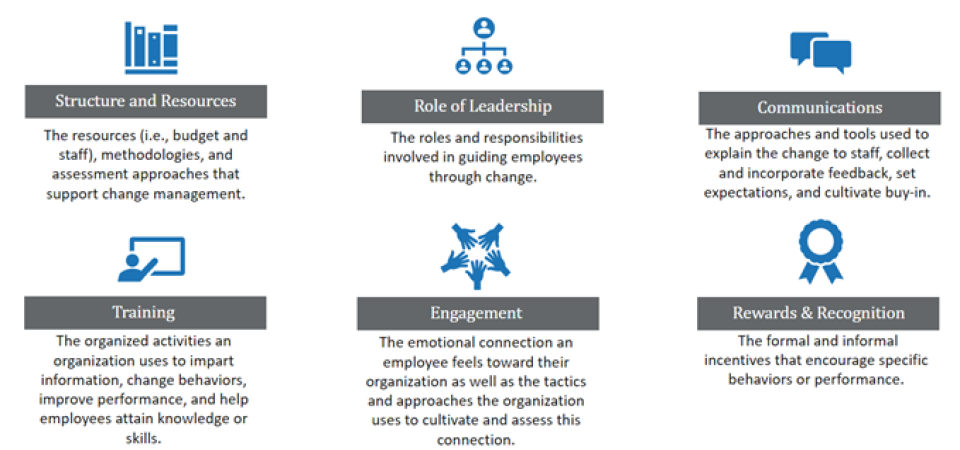
- The role of leadership in change management involves active and visible sponsorship while guiding employees through the transition. Change initiatives are often accompanied by resistance and a variety of emotions; so, when managers can listen, empathize with the employee, mentor and coach, successful change is more likely.
- Structure and resources refer to budget and people with the capability to manage change, the change methodology applied, and the assessment approaches that support change management. Most organizations fall into either a centralized, decentralized, or federated approach to change management. While the type of structure doesn’t affect the overall effectiveness of change, APQC’s research shows that organizations with a federated model have the least resistance to change.
Communications include the approaches and tools used to build awareness of the change, collect and incorporate employee feedback, set expectations, and cultivate buy-in. Best practice organizations ensure they have a phased and documented communication plan, build transparency into messaging about the change and use a variety of methods such as email, town halls, employee forums, videos, and social media.
APQC also found that organizations saw higher change management effectiveness when they tailored messages and communication methods to different audiences depending on their needs and ensured the person communicating is a “meaningful sender”.
- Training involves structured activities an organization uses to impart information, change behaviors, improve performance, and help employees attain knowledge or skills. Organizations typically train employees on the change itself but can also include change management training to help employes understand how to effectively manage through change as an individual. APQC’s research found that more than half of organizations utilize peer-led training and on-the-job training, with one-on-one coaching becoming increasingly popular as well.
- Rewards and recognition include the formal and informal incentives that encourage specific and desired behaviors or performance. These can include pay and formal bonuses and incentives, as well as non-monetary recognition and expressions of thanks. Rewarding individuals for their efforts in change adoption has a significant impact on the outcome. And since different people respond to different incentives, it is important to include an array of monetary and non-monetary forms of reward and recognition. Incorporating desired behaviors into performance reviews is also key. This communicates the message that the new behaviors are a required function of the job.
- Engagement is a very important piece of any change initiative and refers to the emotional connection an employee feels toward their organization as well as the approaches used. Taking the time to learn what motivates—and does not motivate—employees will help leaders and change management teams design effective incentives.
Involving employees early in the change process can ensure employees’ voices are heard and they see the importance of their role in the change. This ultimately reduces resistance and increases buy-in.
Final Thoughts
Managing change effectively has become a focal issue as the workforce faces an ever-increasing rate of change and consequential feeling “change fatigue.” This is why, when implementing your KM program, it is important to include a change approach that includes the six components of change. This will help impact your KM program’s effectiveness, while increasing employee engagement and contributing to your organization’s overall success.
You can learn more about change management by accessing APQC’s collection of research on Making Change Management Mindful and see what Expert Advice on Change Management emerged during a recent panel discussion with member organizations.