Production schedule attainment during a primary products planning period
This measure calculates average production schedule attainment for a planning period for primary (or high level) products. It is part of a set of Process Efficiency measures that help companies optimize the performance of their "produce product" process by minimizing waste and refining resource consumption.
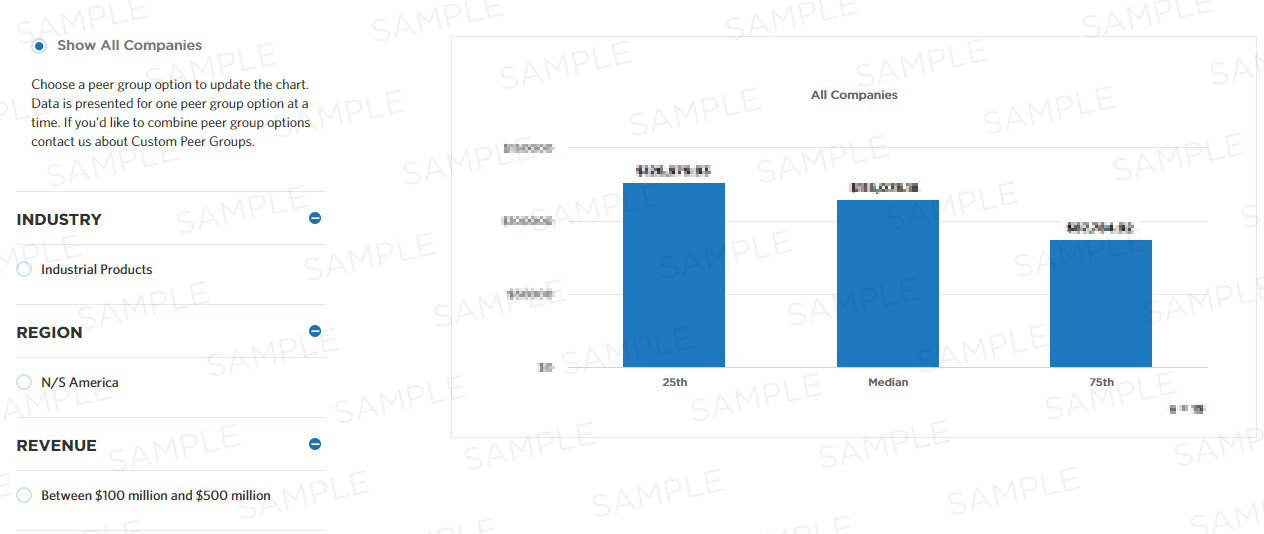
Benchmark Data
Measure Category:
Process Efficiency
Measure ID:
100251
Total Sample Size:
1,681 All Companies
Performers:
| 25th | Median | 75th |
|---|---|---|
| - | - | - |
Key Performance Indicator:
No
Compute this Measure
Units for this measure are percent.
Production schedule attainment during a primary products planning period
Key Terms
Process efficiency
Process efficiency represents how well a process converts its inputs into outputs. A process that converts 100% of the inputs into outputs without waste is more efficient than one that converts a similar amount of inputs into fewer outputs.