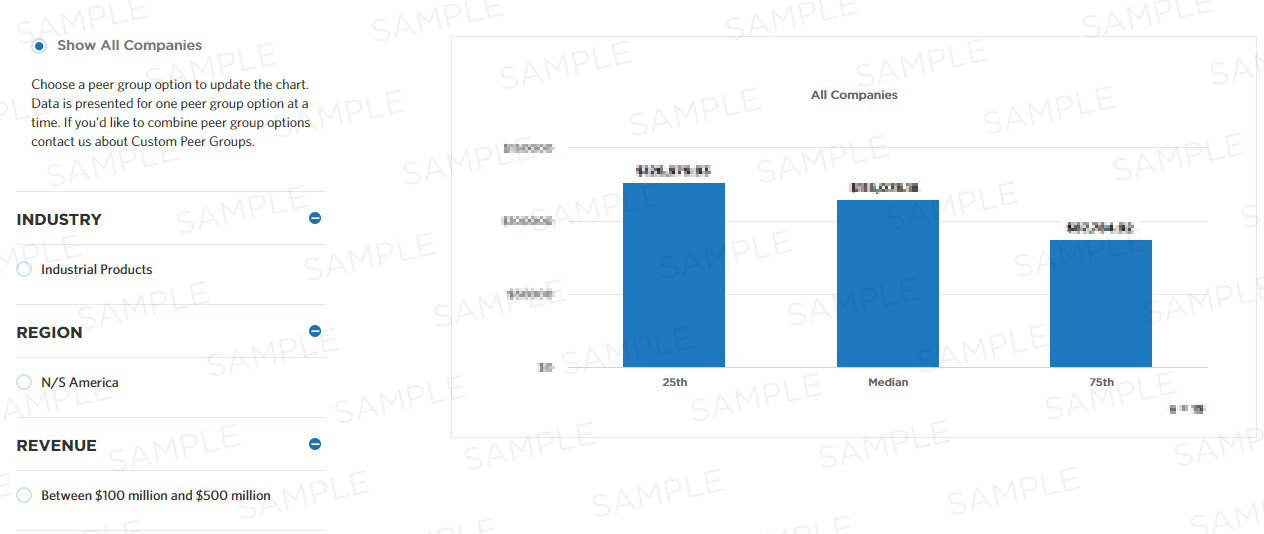
Customer order cycle time in days
This measure calculates the average cycle time in days (including weekends) between order placement by the customer and order delivery to the customer for primary products. Customer Order Cycle Time is equal to Source Cycle Time plus Make Cycle Time plus Deliver Cycle Time). This measure is part of a set of Cycle Time measures that help companies evaluate run times for various parameters within the "deliver products and services" process.
Benchmark Data
Sorry! Not all users have access to all of our resources.
Want to unlock access to all of our resources?
Learn about Membership| 25th | Median | 75th |
|---|---|---|
| - | - | - |
Indicator:
Compute this Measure
Units for this measure are days.
Customer order cycle time in days
Key Terms
Cycle Time
Cycle time is the total time from the beginning of the process to the end. This includes both time spent actually performing the process and time spent waiting to move forward.
Median
The metric value which represents the 50th percentile of a peer group. This could also be communicated as the metric value where half of the peer group sample shows lower performance than the expressed metric value or half of the peer group sample shows higher performance than the expressed metric value.
Measure Scope
Cross Industry (6.1.1)
-
4.1 - Plan for and align supply chain resources (10215) - Creating strategies for production and materials. Handle the demand for the products of the organization. Develop plans for handling materials. Develop and administer the schedule for master production. Plan for distribution requirements and its constraints by reviewing and assessing distribution policies and performance and by establishing quality standards and procedures.
-
4.1.1 - Develop production and materials strategies (10221) - Creating strategies for production processes, as well as the process of managing materials. Define production and supply constraints. Design a blueprint of the workplace. Establish rules and regulations regarding the employees, outsourcing of services, and the expenditure to be incurred on the manufacturing capital.
-
4.1.1.1 - Define manufacturing goals (10229) - Creating quantifiable strategic objectives for each manufacturing segment in conjunction with sales projections.
-
4.1.1.2 - Define labor and materials policies (10230) - Setting up internal rules and regulations regarding the employees and the materials.
-
4.1.1.3 - Define outsourcing policies (10231) - Creating rules and regulations regarding contracting out of a business process to another party in order to reduce costs.
-
4.1.1.4 - Define manufacturing capital expense policies (10232) - Designing rules and regulations pertaining to the expenditure incurred in acquiring or upgrading the existing stock of manufacturing capital.
-
4.1.1.5 - Define capacities (10233) - Outlining the manufacturing and processing capacities of the organization. Delineate the capabilities required for optimizing output with available resources. Analyze capabilities possessed by the organization concerning the raw materials required and the process necessitated for producing finished products.
-
4.1.1.6 - Define production network and supply constraints (10234) - Defining limitations in the ability of the organization's supply chain to deliver a new stock, and creating a network of production stakeholders. Frame and manage relationships within the flow of manufacturing and processing operations. Identify probable supply issues.
-
4.1.1.7 - Define production process (14193) - Outlining the scheme of processing inventory into finished products/services. This includes the use of raw materials, machinery, skill sets, and knowledge to create new offerings.
-
4.1.1.8 - Define production workplace layout and infrastructure (14194) - Determining the floor plans for the processing facility that is meant for delivering finished products/services. Identify the totality of infrastructure needed for using this space in the manufacturing process, including machinery, factory floors, offices, and furniture.
-
-
4.1.2 - Manage demand for products and services (10222) - Forecasting demand for products using secondary research and customer feedback. Refine these forecasts. Inspect the approach used in creating forecasts, and determine its accuracy.
-
4.1.2.1 - Develop baseline forecasts (10235) - Identify the bedrock levels of market demand anticipated for the organization's products/services. Estimate future demand for product and services using historical data, analysis of the market environment and any externalities, etc. to create ex ante approximations.
-
4.1.2.2 - Collaborate with customers (10236) - Working closely with the organization's customers to understand their drives and behavior, with the objective of estimating future demand. Reach out to customers through various means to understand their behavior patterns, usage elasticity, and degree of variability--and ultimately determine demand for each offering.
-
4.1.2.3 - Develop consensus forecast (10237) - Arriving at a consensus over the forecasted levels of demand for products/services. Consensus is achieved by juxtaposing decisions developed in the baseline forecast with those reached at by collaborating with customers. Enlist senior-level decision makers of the sales and marketing functions.
-
4.1.2.4 - Determine available to promise (10238) - Identify the volume of products/services that may be committed for delivery to fulfill sales. Figure out the amount of stock available. Forecast its volumes.
-
4.1.2.5 - Monitor activity against forecast and revise forecast (10239) - Picking out any activity that deviates from the forecast, and adjusting it. Closely track and study the levels of demand as they emerge. Refine the consensus forecast as needed.
-
4.1.2.6 - Evaluate and revise forecasting approach (10240) - Examining the methodology used to estimate future demand. Refine it in light of current market realities and demand.
-
4.1.2.7 - Measure forecast accuracy (10241) - Calculating and inspecting the accuracy of demand forecasts. Use metrics to check the reliability of the forecasts created.
-
-
4.1.3 - Create materials plan (10223) - Developing a scheme that allows for advance planning for the availability of raw materials and spares. Start with an unconstrained plan, and refine based on supply chain realities by identifying critical materials required for production, checking material specifications, and collaborating with all vendors over the supply.
-
4.1.3.1 - Create unconstrained plan (10242) - Developing a plan for raw materials and other inventory items in order to meet market demand. Ensure the availability of all inventory items such as raw materials and spares. Create a blueprint in line with Define labor and materials policies [10230].
-
4.1.3.2 - Collaborate with supplier and contract manufacturers (10243) - Collaborating with vendors and contractual manufacturers with the objective of ensuring a continual supply of raw materials and spares. Leverage long-term connections/relationships with various suppliers, and cultivate new ones. Track the activities of all vendors. Receive regular updates to prepare for any fluctuations in supply.
-
4.1.3.3 - Identify critical materials and supplier capacity (10244) - Identifying principal materials needed for the manufacturing process and the levels of supply that may be ensured for them. Determine the essential and crucial inventory items required for the smooth functioning of all manufacturing processes. Estimate the average, peak, and baseline capacities of various vendors and suppliers. Establish the capability of individual suppliers from the market and the vendors.
-
4.1.3.4 - Monitor material specifications (10245) - Observing and surveying all inventory items in order to check for the veracity of their specifications. Monitor various attributes and characteristics for respective inventory items such as density, volume, and size, as well as contextualized specifications particular to the respective materials.
-
4.1.3.5 - Generate constrained plan (10246) - Generating a bounded plan that takes stock of the actual supply chain scenario. Take stock of all information collected while creating an inventory supply plan.
-
4.1.3.6 - Define production balance and control (14196) - Defining an equitable volume for the production of products/services that adheres to an equilibrium value, and creating a scheme of control for processing items. Create schematics for systematically planning, coordinating, and directing the manufacturing activities in line with the production balance determined.
-
-
4.1.4 - Create and manage master production schedule (10224) - Taking care of the master production plan. The master production includes creation and implementation of the site-level production plan, as well as management of the inventory that is currently in the production process.
-
4.1.4.1 - Create site-level production plan and schedule (10247) - Developing a plan and schedule for managing site-level production. Develop a timeline of activities to perform at the production site. Decide the timing and duration of every on-site activity.
-
4.1.4.2 - Manage work-in-progress inventory (10248) - Handling the inventory attached with the production activities in-progress. Monitor every item of inventory being produced. Supervise the use of materials/raw materials in production to promote judicious and efficient use.
-
4.1.4.3 - Collaborate with suppliers (10249) - Creating and maintaining relationships with the suppliers of materials/raw materials to ensure smooth and timely supply of these materials for the production process.
-
4.1.4.4 - Execute site-level production plan and schedule (10250) - Implementing the site-level production plan by following the timeline of activities. Monitor the timing and duration of every activity to avoid any fallback on the predefined schedule.
-
4.1.4.5 - Monitor master production schedule and plan (17041) - Supervising and overseeing the plan for internal activities such as production, inventory, and staffing. Set the quantity of items to produce each week of a short-range planning horizon.
-
-
4.1.5 - Plan distribution requirements (17042) - Maintaining master data of finished products and inventory. Identify the requirements of finished products at the destination, as well as partner requirements. Calculate the consolidation at source. Manage replenishment planning. Create and administer a dispatch plan. Calculate load plans for destinations and partners. Manage the cost of supplying these products. Ensure effective utilization of capacity.
-
4.1.5.1 - Maintain master data (10252) - Maintaining and preserving the master data plan for distribution requirements. Create a systematic collection of facts and figures regarding the distribution of the inventories. Maintain policies, processes, and tools covering the distribution function.
-
4.1.5.2 - Determine finished goods inventory requirements at destination (10253) - Interact with the concerned person at the destination to validate the requirements and to avoid any miscommunication of information.
-
4.1.5.3 - Calculate requirements at destination (10254) - Interact with the concerned authority at the destination to reach a specific figure that correctly represents requirements.
-
4.1.5.4 - Calculate consolidation at source (10255) - Determining the aggregate volume of products/services consolidated at the source. Calculate the number of finished products that are ready to be delivered to the customers, particularly at one date.
-
4.1.5.5 - Manage collaborative replenishment planning (10256) - Administering the plan for collaborative replenishment of goods. Replenish inventory by creating a plan in case of faulty production.
-
4.1.5.6 - Manage requirements for partners (10257) - Associating with partners to simplify and increase the efficiency of the process. Take care of the specific inventory requirements for all the partners. Ensure the timely dispatch and receiving of the inventory.
-
4.1.5.7 - Calculate destination dispatch plan (10258) - Estimating the timing and duration of the delivery of the inventory from the source to the destination. Plan the logistic details of all the distribution routes and activities.
-
4.1.5.8 - Manage dispatch plan attainment (10259) - Accomplishing the dispatch plan. Strictly follow the schedule, and adjust for deviations. Coordinate with the concerned authorities at various destinations.
-
4.1.5.9 - Calculate destination load plans (10260) - Evaluating the plans for delivering loads to destinations. Create a systematic plan that specifies the load plans for every single destination.
-
4.1.5.10 - Manage partner load plan (10261) - Administering the load plan for partners. Manage the delivery, and dispatch from the source to the partners.
-
4.1.5.11 - Manage cost of supply (10262) - Managing all expenses to provide products/services in the market. Estimate the overall cost of supplying of products/inventory, including the cost distributing it through various partners and channels. Consider the cost of all the logistical processes that occur from the moment a product is ready to be dispatched to the time it reaches the destination.
-
4.1.5.12 - Manage capacity utilization (10263) - Determining the capacity utilization of the organization's production process. Realize the extent to which an enterprise uses its installed productive capacity (i.e., the relationship between output and the potential output if capacity was fully used).
-
-
4.1.6 - Establish distribution planning constraints (10226) - Instituting the constraints for planning of distribution process. Create a plan that specifies every element in the distribution process from the blueprint of the distribution centers to how and when the inventory would reach the distribution centers.
-
4.1.6.1 - Establish distribution center layout constraints (10267) - Instituting the constraints for creating a layout for distribution center. Consider factors such as the number of customers, demand forecasting, product groups, condition of product conservation, warehousing, and transportation management.
-
4.1.6.2 - Establish inventory management constraints (10268) - Determining any problems that might be faced while managing inventory. Identify problems and possible issues in managing the warehousing of the raw materials, spares, and other items of inventory. Take stock of inventory needs, and determine the exact quantity of the inventory needed in the near future.
-
4.1.6.3 - Establish transportation management constraints (10269) - Identifying any potential constraints while deciding on the dispatch and delivery plan from the source to the various distribution centers. Decide how the inventory will be transported , which and how many transportation means to use, what route to take, etc.
-
-
4.1.7 - Review distribution planning policies (10227) - Revisiting and refurbishing the policies for planning the distribution process. Asses the distribution strategies, including how the products are to be made available and sent to different distributors. Set guidelines regarding relationships between the sources and the distribution centers.
-
4.1.7.1 - Review distribution network (10264) - Evaluating the system that defines how the products/inventory would reach from the source (i.e., manufacturer) to the destination (i.e., retailer/distributer).
-
4.1.7.2 - Establish sourcing relationships (10265) - Establishing relationships with transportation/distribution sources in order to ensure an effective distribution network and strategy. Screen and evaluate various sources available to pick out the best among them.
-
4.1.7.3 - Establish dynamic deployment policies (10266) - Creating strategic guidelines on the availability of the products at all the distribution centers. Create a dynamic network to ensure availability at all times, even in cases of defaults.
-
-
4.1.8 - Assess distribution planning performance (10228) - Evaluating the performance of distribution plans. Establish appropriate indicators, using them to evaluate performance gaps. Create a performance improvement plan for the distribution system.
-
4.1.8.1 - Establish appropriate performance indicators (metrics) (10270) - Designing key measures that analyze and interpret how effectively the business is achieving its objectives.
-
4.1.8.2 - Establish monitoring frequency (10271) - Deciding on the appropriate amount of supervisions that are needed to effectively assess the performance of business plans.
-
4.1.8.3 - Calculate performance measures (10272) - Measuring the performance of process planning. Quantify the performance, record results of the performance tests, and report them to the appropriate authority.
-
4.1.8.4 - Identify performance trends (10273) - Recognizing the trends in performance. Carefully and strategically assess the results in order to effectively spot the trends.
-
4.1.8.5 - Analyze performance benchmark gaps (10274) - Evaluating the gaps between achieved and benchmarked performance. Analyze how performance differs from the optimal or expected performance.
-
4.1.8.6 - Prepare appropriate reports (10275) - Creating reports that systematically record and represent the performance planning. Construct a detailed report specifying the performance, and include indicators such as the performance gaps, performance trends, and analysis.
-
4.1.8.7 - Develop performance improvement plan (10276) - Using performance indicators to report, analyze, and create a detailed performance improvement plan to bridge the performance gaps.
-
-
4.1.9 - Develop quality standards and procedures (10368) - Developing standards and procedures for maintaining the quality of products/services. Establish desired quality targets. Create standardized procedures for the quality. Ensure quality specifications are effectively communicated.
-
4.1.9.1 - Establish quality targets (10371) - Defining specific qualitative and quantitative target figures.
-
4.1.9.2 - Develop standard testing procedures (10372) - Creating standard procedures for testing the quality of products/services. Describe the steps of key processes to help ensure consistent and quality output. Define the routine instructions for performing the quality testing activity.
-
4.1.9.3 - Communicate quality specifications (10373) - Communicating the desired quality specifications to the manufacturing units, as well as the distribution centers, to avoid any misunderstanding or misinterpretation.
-
-
-
4.2 - Procure materials and services (10216) - Creating a plan for procuring materials and services. Develop strategies for sourcing materials and services. Choose the most appropriate suppliers, and develop contracts with them. Order the materials and services as per the requirements. Manage relationships with suppliers.
-
4.2.1 - Develop sourcing strategies (10277) - Creating strategies for procuring materials and services from various sources, and for managing and evaluating categories. Establish a procurement process that describes the approach for obtaining products and purchasing activities. Evaluate the sources. Create sourcing relationships in order to continuously improve. Re-evaluate purchasing activities.
-
4.2.1.1 - Develop procurement plan (10281) - Creating a plan for procuring materials and services. Plan what to buy, when, and from what sources. Include project requirements, the procurement team, the justification for the procurement, a timeline of events, and an explanation of the supplier selection process. Outline specific actions to start and complete purchases in order to adhere to best practices.
-
4.2.1.2 - Clarify purchasing requirements (10282) - Defining the purchasing requirements for materials and services. Specify the exact inventory required for the production process. Create a specific quotation for all the sources in order to avoid any duplication or overlap.
-
4.2.1.3 - Develop inventory strategy (10283) - Developing a strategy to deal with issues projected to arise during implementation of the inventory plan. Identify how to react to issues that arise and require changes to the inventory plan, such as a vendor failing to deliver materials on time. Collaborate with production and suppliers to prepare solutions to projected problems.
-
4.2.1.4 - Match needs to supply capabilities (10284) - Synchronizing the requirements of materials and services and the capacity of suppliers for providing these materials and services. Revamp the procurement needs of the company in consideration of the capabilities of the suppliers.
-
4.2.1.5 - Analyze organization's spend profile (10285) - Evaluating the spend profile of the organization. Collect, cleanse, classify, and analyze the procurement data with the purpose of reducing procurement costs, improving efficiency, and monitoring compliance.
-
4.2.1.6 - Seek opportunities to improve efficiency and value (10286) - Seeking the most efficient sourcing and procurement opportunities.
-
4.2.1.7 - Collaborate with suppliers to identify sourcing opportunities (10287) - Collaborating with the suppliers of materials and services in order to determine new opportunities for sourcing.
-
-
4.2.2 - Select suppliers and develop/maintain contracts (10278) - Evaluating supplier options to select the most effective and efficient suppliers. Validate selected suppliers. Establish and manage supplier contracts.
-
4.2.2.1 - Select suppliers (10288) - Evaluating the pros and cons of various suppliers. Choose the most appropriate and cost-effective suppliers on the basis of their material quality, delivery schedules, and costs.
-
4.2.2.2 - Certify and validate suppliers (10289) - Validating the supply sources, and provide certification as an official supplier.
-
4.2.2.3 - Negotiate and establish contracts (10290) - Legally binding suppliers with the company. Negotiate contracts individually with all the suppliers that include the promised material delivery, the delivery dates and duration, etc.
-
4.2.2.4 - Manage contracts (10291) - Keeping contracts up-to-date with routine evaluation. Maintain order and discipline with the contracts in order to avoid any loss of information and mishaps.
-
-
4.2.3 - Order materials and services (10279) - Creating and approving requisitions and distributing purchase orders accordingly. Hasten the procurement process to satisfy internal needs.
-
4.2.3.1 - Process/Review requisitions (10292) - Handling operations related to processing/reviewing the requisitions. Establish and maintain procedures for the initiation, authorization, and processing of purchase requirements to procure products/services.
-
4.2.3.2 - Approve requisitions (10293) - Approving requisitions for materials and services. Examine distributor-specific requests, and validate them individually.
-
4.2.3.3 - Solicit/Track vendor quotes (10294) - Requesting quotes from suppliers. Use a request for quotation (RFQ) to invite suppliers into a bidding process for specific products/services.
-
4.2.3.4 - Create/Distribute purchase orders (10295) - Creating and placing the orders for purchasing materials and services from suppliers. Analyze vendor quotes. Choose the most cost-effective vendors. Create vendor-specific orders. Distribute them in order to initiate the purchasing process.
-
4.2.3.5 - Expedite orders and satisfy inquiries (10296) - Accelerating the purchase orders in order to fulfill the internal needs (for raw materials) depicted through inquiries.
-
4.2.3.6 - Record receipt of goods (10297) - Verify that purchase orders are filled as expected: verify that items and quantities are delivered as expected, based on purchase order details and goods receipts.
-
4.2.3.7 - Research/Resolve exceptions (10298) - Identifying and resolving any exceptions. Address the internal needs/inquiries for materials that cannot be procured immediately. Research inquiries that require the need of exceptional materials.
-
-
4.2.4 - Manage suppliers (10280) - Collecting and analyzing new information in order to track and rate suppliers through a supplier information management system.
-
4.2.4.1 - Monitor/Manage supplier information (10299) - Examining procurement and vendor performance. Report delivery timing and the quality of the materials procured through different vendors.
-
4.2.4.2 - Prepare/Analyze procurement and vendor performance (10300) - Assisting the production and inventory processes through the information and reports created. Use the information and metrics of the procurement and vendor performance to enhance or improve the production process.
-
4.2.4.3 - Support inventory and production processes (10301) - Support inventory and production processes by analyzing impact of procurement decisions and collaborating to constantly improve. (For example, perhaps minimum order requirements could be negotiated to be lower, to reduce excessive inventory and make production more flexible.)
-
4.2.4.4 - Monitor quality of product delivered (10302) - Track the performance of the suppliers on product quality. Use this information to further improve sourcing and supplier performance.
-
-
-
4.3 - Produce/Manufacture/Deliver product (10217) - Processing and delivering the finished goods manufactured by the organization. Schedule the production of products. Execute the product production activities. Perform tests to oversee and ensure quality of production. Maintain records of the production process. Track lots.
-
4.3.1 - Schedule production (10303) - Scheduling the production of final products. Generate a detailed schedule plan. Create and release production orders and lots. Schedule the planned and unplanned maintenance orders.
-
4.3.1.1 - Generate line level plan (10306) - Initiating the line-level plan for production. Break down the production schedule into specific lines, specifying the various objectives the production schedule.
-
4.3.1.2 - Generate detailed schedule (10307) - Broadening the line-level plan. Specify all the individual production processes, along with the timing and the duration to come up with a working schedule that tracks the whole process and any deviations that might occur.
-
4.3.1.3 - Schedule production orders and create lots (10308) - Creating a schedule to commence production of orders received, and creating lots to consolidate the processing. Plan when the production orders are to be initiated by commencing the operations for processing products/services. Specify which materials to produce, where to produce them, which operations will facilitate this, and on which date production is to start. Define the size of production lots, demarcating the durations of batch production.
-
4.3.1.4 - Schedule preventive (planned) maintenance (preventive maintenance orders) (10315) - Scheduling planned maintenance of the production equipment.
-
4.3.1.5 - Schedule requested (unplanned) maintenance (work order cycle) (10316) - Scheduling requested maintenance in order to address breakdowns where repairs or corrective remedies are needed immediately. Create a scheme for undertaking unplanned maintenance work on equipment/machinery that has come to be in urgent need for it. Express turnaround to redress using specialized personnel.
-
4.3.1.6 - Release production orders and create lots (10309) - Initiating the delivery of production orders, and creating lots. Communicate the order that specifies which material to produce, where to produce it, which operations to require, and on which date production takes place. Define how to settle the order costs. Create production lots, which is a particular production unit of an assembly that is planned and manufactured.
-
-
4.3.2 - Produce product (10304) - Manufacturing the product. Convert the raw materials to develop consumer-ready products. Manage the raw materials to implement the detailed production schedule. Reproduce defectives to establish and remediate cause. Ensure production optimization and benchmark performance.
-
4.3.2.1 - Manage raw material inventory (10310) - Administering the inventory of raw materials. Manage the total cost of all component parts in stock but not yet used. Manage the cost of the direct materials (i.e., materials incorporated into the final product) and indirect materials (i.e., materials not incorporated into the final product but consumed during the production process).
-
4.3.2.2 - Execute detailed line schedule (10311) - Creating and implementing the detailed line production schedule on the ground level.
-
4.3.2.3 - Report maintenance issues (10319) - Recording and reporting any deviations or issues in the maintenance schedule, in the performance to the production management team, and for unplanned maintenance.
-
4.3.2.4 - Rerun defective items (10313) - Reproducing the items produced defectively. Assess the produced items by conducting quality and standardization tests in order to diagnose any discrepancies. Reproduce defective items.
-
4.3.2.5 - Assess production performance (10314) - Analyzing and benchmarking the production process to judge its effectiveness and efficiency. Create production metrics to numerically calculate the performance of the production process.
-
-
4.3.3 - Perform quality testing (10369) - Executing tests to evaluate the quality of the products manufactured. Calibrate the test equipment. Conduct the actual tests. Record the results and outcomes of the quality test conducted.
-
4.3.3.1 - Calibrate test equipment (10318) - Regulating the equipment used for performing quality tests. Assess correspondence between the quality testing equipment and the desired quality standards. Ensure the calibration standard is more accurate than the instrument being tested.
-
4.3.3.2 - Perform testing using the standard testing procedure (10374) - Performing testing using calibrated equipment and in consent with the standard testing procedure, including testing time.
-
4.3.3.3 - Record test results (10375) - Documenting the results and outcomes of the quality tests. Track the performance of the production process. Record/Document it to evaluate the qualitative efficiency of the production process. Use electronic devices and software in order to ensure effectiveness in recording the results and outcomes of the test.
-
-
4.3.4 - Maintain production records and manage lot traceability (10370) - Perpetuating the production records by systematically documenting and using it to ensure the effective management of lots. Determine the lot numbering system and its use. (The lot number enables tracking of the constituent parts, as well as labor and equipment records involved in the manufacturing of a product. It enables manufacturers and to perform quality control checks, calculate expiration dates, and issue corrections of their production output.)
-
4.3.4.1 - Determine lot numbering system (10376) - Allotting an identification number to a particular quantity or lot of material manufactured. Assign lot numbers on the basis of specific production units, material similarity, etc. Place lot numbers on the outside of packaging.
-
4.3.4.2 - Determine lot use (10377) - Identifying the use of production lots. Define where, how, and when to use a specific production lot.
-
-
-
4.4 - Deliver service to customer (10218) - Validating specific service requirements for individual customers. Determine and schedule resource to fulfill these requirements. Provide service to specific individual customers. Ensure the quality of service delivery.
-
4.4.1 - Confirm specific service requirements for individual customer (10320) - Acquiring or soliciting information about specific service requirements for individual customers through the customer service function. Obtain information about customer specific requests, process these requests, and create customer profiles to generate a service order.
-
4.4.1.1 - Process customer request (10324) - Soliciting or acquiring information using various sources such as databases, customer interactions, and customer request forms. Hand them further up the hierarchy to deal with them. Categorize the user's request, determining if the request is supportable and prioritizing the request.
-
4.4.1.2 - Create customer profile (10325) - Documenting the individual customer service requirements solicited, along with personal information of the customers, in order to generate customized profiles that hasten the delivery process.
-
4.4.1.3 - Generate service order (10326) - Designing a short-term agreement between the service provider and customer. One-time services are ordered by the service recipient and resource-related billing is performed upon completion. Use the service order to document service and customer service work.
-
-
4.4.2 - Identify and schedule resources to meet service requirements (10321) - Determining and scheduling the resources required to fulfill customer service requirements. Create a detailed schedule about the service orders and development of these service orders.
-
4.4.2.1 - Create resourcing plan and schedule (10327) - Developing a plan for sourcing and deploying the resources required to fulfill customer service needs. Document a detailed summary of all types of resources (equipment, finance, personnel, time, etc.) required to complete customer service requests and procure these resources. Identify and assess various sources in order to effectively create a resourcing plan.
-
4.4.2.2 - Create service order fulfillment schedule (10328) - Designing a detailed summary of customer service order requirements, along with information concerning the timing and duration for these services. Categorize the customer needs. Monitor the services delivered.
-
4.4.2.3 - Develop service order (10329) - Creating contracts for the provision of services offered by the organization. Develop an agreement with service recipients, which ensures on-time services to recipients. Specify data groups such as header data, location and account assignment data, object data, settlement data, operation data, and component data.
-
-
4.4.3 - Provide service to specific customers (10322) - Dispatching resources for managing and fulfilling daily service requirements. Manage the progress of order fulfillment. Complete order blocks.
-
4.4.3.1 - Organize daily service order fulfillment schedule (10330) - Laying out a daily plan of specific service orders that need to be fulfilled. Document and systematically order these activities to ensure high effectiveness and efficiency.
-
4.4.3.2 - Dispatch resources (10331) - Dispatching and delivering the resources needed for the specific service requirements from the source/warehouse. Manage the dispatch, transportation, and delivery of the services.
-
4.4.3.3 - Manage order fulfillment progress (10332) - Handling and managing orders fulfilled, along with the orders are not or partially fulfilled to track the order fulfillment progress. Use electronic devices such as trackers and GPS in order track and ensure delivery of the orders.
-
4.4.3.4 - Validate order fulfillment block completion (10333) - Validating the complete fulfillment of service orders committed, in blocks for ease of tallying. Check the status of orders through a centralized tracking register as well as with project timesheets, by checking for the identification codes associated with individual work orders and with the order blocks.
-
-
4.4.4 - Ensure quality of service (10323) - Guaranteeing the quality of service provided to customers. Identify the successful and unsuccessful orders along with the service failures. Collect customer feedback. Process the feedback to ensure the quality of service in the future.
-
4.4.4.1 - Identify completed orders for feedback (10334) - Determining the service orders that have been successfully delivered. Identify the service orders completed and delivered to the customer. Leverage communication systems to ensure coordination with the customers in order to avoid mishaps.
-
4.4.4.2 - Identify incomplete orders and service failures (10335) - Determining orders which have not been completed or delivered. Identify the service orders that are partially or entirely incomplete, as well as the orders that have not been delivered to the customer. Use techniques such as project trackers to recognize the progress of the service orders.
-
4.4.4.3 - Solicit customer feedback on services delivered (10336) - Obtaining and procuring customer reviews or feedback on the services delivered. Design a customer feedback form, or communicate with the customer through the phone or online.
-
4.4.4.4 - Process customer feedback on services delivered (10337) - Assessing and incorporating customer reviews/feedback into the service plan to ensure high quality of service.
-
-
-
4.5 - Manage logistics and warehousing (10219) - Administering and overseeing all activities related to logistics and warehousing. Outline and establish a strategy for the logistics function. Plan and administer the flow of inbound materials. Administer the operational activities of warehousing and outbound transportation. Manage reverse logistics including returns and exchanges.
-
4.5.1 - Define logistics strategy (10338) - Outlining the strategy for managing logistics. Translate customer requirements logistic requirements. Create an efficient logistic network and outsourcing portions of logistics activities. Design a logistics strategy that optimizes transportation costs and schedule. Define key performance indicators.
-
4.5.1.1 - Translate customer service requirements into logistics requirements (10343) - Determining the requirements for managing the flow of things between the point of origin and the point of consumption by assessing the service requirements of the customers.
-
4.5.1.2 - Design logistics network (10344) - Developing a network for logistical activities. Create a network of entities through which materials and information flow, encompassing all related activities associated with the flow of transformation of products.
-
4.5.1.3 - Communicate outsourcing needs (10345) - Conveying outsourcing needs within the organization, with the objective of sourcing the assistance required. Define the portion of logistical activities that can be transferred to outside suppliers. Assess third-party agencies to carefully select the most appropriate agencies for outsourcing. Convey these needs to management or the appropriate authority.
-
4.5.1.4 - Develop and maintain delivery service policy (10346) - Establishing rules and regulations, as well as the terms and conditions regarding the delivery of service by the company. Develop a delivery plan that specifies what, how, when, and in which way to deliver services to the customer.
-
4.5.1.5 - Optimize transportation schedules and costs (10347) - Optimizing the schedule and costs of transportation services. Design a logistics strategy by strategically creating delivery routes and systems, which optimizes the overall transportation schedules and costs. Evaluate different transportation sources in order to select the most appropriate and cost-effective sources.
-
4.5.1.6 - Define key performance measures (10348) - Establishing measures for evaluating the performance of the logistics strategy of the organization. Establish key performance indicators, including the logistics performance index, delivery in full, and delivery on time.
-
-
4.5.2 - Plan and manage inbound material flow (10339) - Working out the receipts of the inbound materials. Supervise the inbound delivery processes. Judge its efficiency. Take care of the deviations such as defective and incorrectly delivered products/materials.
-
4.5.2.1 - Plan inbound material receipts (10349) - Managing the receipts of inbound materials. Create a plan accounting for the materials procured from the source of supply and the materials delivered to the distribution center or the warehouse.
-
4.5.2.2 - Manage inbound material flow (10350) - Managing all the internal activities related to the flow/transfer of materials. Manage materials being delivered to distribution center or warehouse. Gauge the time taken for delivery and if the delivery process is on time.
-
4.5.2.3 - Monitor inbound delivery performance (10351) - Overseeing the performance of an inbound delivery system. Check the present delivery system's efficiency, cost effectiveness, and adherence to a delivery schedule.
-
4.5.2.4 - Manage flow of returned products (10352) - Tracking and taking care of the products that have been internally returned either because of their deficiency or in cases of incorrect delivery.
-
-
4.5.3 - Operate warehousing (10340) - Tracking the inventory deployment. Accept and store products. Ship the products. Measure the accuracy of the inventory. Assess the performance of the outsourced logistics activities.
-
4.5.3.1 - Track inventory deployment (10353) - Tracking the logistical act of delivering or releasing an inventory item or entity to targeted end users. Track how much inventory has been deployed at all the distribution centers, individually.
-
4.5.3.2 - Receive, inspect, and store inbound deliveries (10354) - Coordinating the incoming inbound materials/products. Accept the delivery of these materials and the subsequent storage. Track them at the warehouse/distribution center.
-
4.5.3.3 - Track product availability (10355) - Keeping track of the availability of different materials/products at the warehouse and distribution centers.
-
4.5.3.4 - Pick, pack, and ship product for delivery (10356) - Packing and shipping the product to deliver to the customer. Take care of the internal and external packaging of the products in order to ensure safe transportation of the products from the warehouse to delivery locations. Notify the ERP system and/or Accounts Receivable Dept.
-
4.5.3.5 - Track inventory accuracy (10357) - Monitoring any discrepancies between electronic records that represent the inventory and the physical state of the inventory. Look for discrepancies such as phantom inventory, which includes products that an inventory accounting system considers to be available at the storage location but are not actually available.
-
4.5.3.6 - Track third-party logistics storage and shipping performance (10358) - Keeping a track on the storage and shipping performance of third-party agencies. Monitor logistics storage and shipping performance for third-party agencies. Use measures such as a logistics scoreboard, activity-based costing, economic value analysis, and balanced scorecards.
-
4.5.3.7 - Manage physical finished goods inventory (10359) - Administering the movement of the finished products that are processed by the organization through its warehouses. Track goods through the use of systems such as barcodes in order to monitor the volumes available, quantity of out-flowing goods, remaining shelf life of the product, etc.--ultimately, to best manage the warehouse capacity.
-
-
4.5.4 - Operate outbound transportation (10341) - Creating a plan that specifies the schedule and system for transportation and delivery of the outbound products, as well as tracking the performance of the carrier delivery system. Conduct vehicle management and processing of all carrier-related documents.
-
4.5.4.1 - Plan, transport, and deliver outbound product (10360) - Organizing the transportation and delivery of outbound products. Plan and organize the transportation, shipping, and delivery of the end products. Create a plan that specifies dispatch and delivery of the product to its destination, as well the transportation.
-
4.5.4.2 - Track carrier delivery performance (10361) - Monitoring delivery performance when carrying products from the warehouse/distribution centers to the retailers or end consumers. Create a performance metrics based on the key performance indicators.
-
4.5.4.3 - Manage transportation fleet (10362) - Taking care of a range of functions related to the means of transport used for delivering the end products. Manage vehicle financing, vehicle maintenance, vehicle telematics (tracking and diagnostics), driver management, speed management, fuel management, and health and safety management.
-
4.5.4.4 - Process and audit carrier invoices and documents (10363) - Organizing and inspecting all account statements and any other documentation for the carriers used in delivery. Create, manage, and inspect all documents related to the financial, regulatory, and administrative accounts of all the carriers/freights. Generate receipts for all freight transactions.
-
-
4.5.5 - Manage returns; manage reverse logistics (10342) - Managing the process of a customer taking previously purchased merchandise back to the retailer. Remit a refund in the original form of payment, exchange for another item (identical or different), or a store credit. Perform reverse logistics and the repair/refurbishment.
-
4.5.5.1 - Authorize and process returns (10364) - Approving and carrying forward the requests by the customers to return the product. This is part of the process of returning a product in order to receive a refund, replacement, or repair during the product's warranty period.
-
4.5.5.2 - Perform reverse logistics (10365) - Moving products from their typical final destination to the origin or manufacturing destination for the purposes remanufacturing or refurbishment. Implement a transportation system to ensure that the products are returned back to their originating position safely and in tact.
-
4.5.5.3 - Perform salvage activities (10366) - Executing activities for reinstating the returned products. Present the customer with additional incentives of compensation in case of any defective products delivery or any discrepancy in the product specifications in order to save the order from being permanently returned.
-
4.5.5.4 - Manage and process warranty claims (10367) - Managing and administering any claims on the warranty of products. Handle and approve the customer claims for repair or replacement of, or compensation for non-performance or under-performance of an item, as provided for in the warranty document.
-
4.5.5.5 - Manage repair/refurbishment and return to customer/stock (14195) - Administering the reinstatement of the returned product in order to return them back to customers. Repair or remanufacture the defective or ineffective products returned by the customer. Process the delivery of the repaired or remanufactured products back to the customer.
-
-